|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Climatefarming |  |
Definition Climate Farming
Climate farming uses agricultural means to keep carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses from escaping into the atmosphere. Like organic farming, climate farming maintains biodiversity and ecological balance on productive, argicultural land. But climate farmers like Hans-Peter Schmidt go a step further and covert leftover organic mass into biochar, a solid carbon compound that can improve soil quality. Biochar production also creates a kind of gas that can then be burned to help generate power. A climate farm could grow food, generate power, and help keep carbon out of the air. . hear the storyClimatefarming - see the film from http://worldradio.ch
Climatefarming is often described as an agricultural method whereby CO2 is removed from the atmosphere and stored permanently in the soil as carbon. This could help slow climate change.But climatefarming is also a way forward to the sustainable agriculture of the future: producing food, energy and clean air while promoting biodiversity and protecting landscapes.
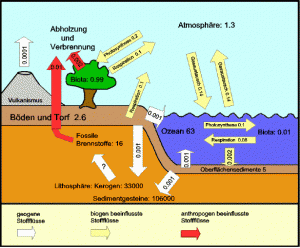
Through their leaves, plants collect carbon dioxide from the air. Using light, minerals, and water molecules plants convert that carbon dioxide into carbon. When the plant dies and decays, or if it is eaten and digested, the long molecules of carbon are split.

______________
This process releases energy, and the carbon, which comprises more than 99% of the CO2, evaporates into the atmosphere.
The natural carbon cycle is now virtually complete. The residual carbon, which does not evaporate into the atmosphere, is stored as humus, peat, oil, natural gas and sediment. But over time, this carbon is also bound to the cycle returned due to volcanic eruptions, climate action, fire and erosion, so
it is indeed a extremely stable.
Because of human intervention, the natural carbon cycle has lost its balance. Since the beginning of the industrial
era we have been burning fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, that used to be stored permanently in the soil. More than 500 billion tonnes of
carbon have been emitted into the atmosphere as CO2. But this is not the only human intervention in the carbon cycle.
___________
____________

Humus stores carbon, water and nutrients, is a habitat for microorganisms, and protects against erosion
Since the beginning of human settlement, nearly half the world's forests have been cleared. Even today, the forest is decreasing by 130,000 km2 per year (approximately 8 times the total surface area of Switzerland). Carbon that was once stored in these forests, trees, shrubs, plants and soils has escaped into the atmosphere. And don't forget this: our remaining soil has lost most of its humus content. Land has been cleared in order to be covered by buildings, streets, and industrialized agriculture. This development has already caused 100 billion tons of carbon to escape from soil into the atmosphere.
Our climate depends less on what is in the atmosphere than on what happens below the earth's surface. Approximately four fifths of the global carbon reserves are stored in soils. Frequent plowing, heavy farm equipment, widespread use of fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides, monoculture farming and the lack of erosion protection: all of this has dramatically lowered the humus content of agricultural land by an average of 70% since the 1950's. These agricultural methods damage the complex network of life in the soil. Soil microbes, needed for the health of plants, are practically wiped out. Compared to healthy soils, only about one in one thousand survives. Significant amounts of carbon are also stored in the cells of more complex soil organisms. Their destruction leads to additional carbon losses..

Mixed crops: potatoes between vines, flowers and bees
__________________
Increasing of humus content of our soil is critical, and not only because of global warming. We can guarantee food and energy security for an earth population of 9 billion with the help of healthy, humus-rich soils while protecting biodiversity. High humus content is an unmistakable sign of ecosystem balance and a healthy habitat. To achieve this, the overall concept of the ecological economic climatefarming was developed. Climatefarming:
- Ends agricultural monocultures
- Increases and protects biodiversity in soils and crops
- Inreases agricultural and economic yield
- Vegetables, fruits, trees, shrubs, herbs, wine, flowers, mushrooms, bees, livestock, and energy crops are complementary to each other
Optimizes material cycles using green manure, compost and Biochar - No need for artificial fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides
- Plant self-defense mainly through the strengthening of biological diversity and eco-friendly resources.
- Creates heat and power by solar, wind and biomass
- Creates carbon sinks in soils due by pyrolysis: creating biochar from biomass residues
- Maintains the diversity of species and varieties, protecting rare and ancient plant species
- Human agriculture and energy production in harmony with nature
Climatefarming is no longer a utopia, but is a fact of life in many places. This short film by Amy Wong gives and example (in English): http://bit.ly/cV8zYE
Climate farmer Hans-Peter Schmidt plot shows the difference in climate-farmed soil (left) from his vineyard and traditional vineyard soil (right) from his neighbor's. June 20, 2009.
Journal für Terroirwein und Biodiversität, 2008, ISSN 1663-0521
Dieser Eintrag wurde veröffentlicht am Samstag, Juli 4th, 2009
More about climatefarming:
Wundererde
Im Grünen vom Dienstag, 15.12.2009 | 18.15 Uhr | SWR Fernsehen in Rheinland-Pfalz
Support the Huntsville Petition
|